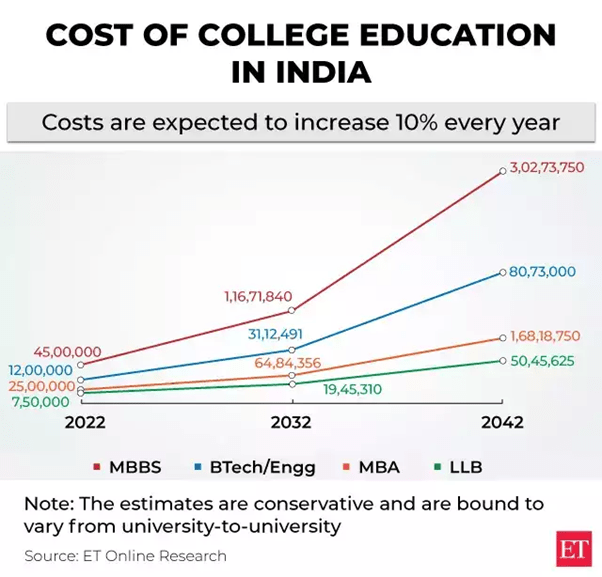
Education has long been the cornerstone of personal and professional success in India. From early schooling to higher education, families across the country invest time, emotion, and substantial financial resources to secure brighter futures for their children. Yet, in recent years, education costs in India have risen at an annual rate of 10–12%, outpacing the country’s overall inflation. This sharp spike, though burdensome for many households, signals a mature and expanding education market ripe with opportunities for both domestic and international investors.
Punjab, with its progressive policies, large youth population, and growing demand for quality education, is quickly emerging as one of the most attractive regional destinations within India for education sector investment. This blog explores the cost dynamics of Indian education, the structural ecosystem, and why states like Punjab offer compelling prospects for investors.
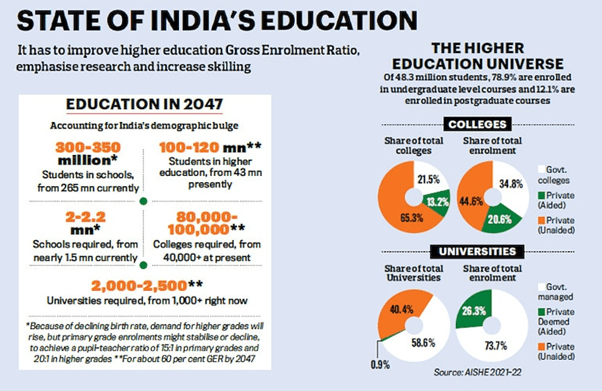
Why the Indian Education Sector Is Attracting Investment
India has the world’s largest population in the 5–24 age group (~500 million). With an increasing aspiration among middle-class families for high-quality education and career readiness, the demand for advanced learning models, digital platforms, and skill development institutions is booming.
Key Drivers of Investment Interest:
Rising Private Expenditure
With public institutions unable to meet demand, families are turning to private schools and coaching centers, which are flourishing. An estimated 70% of urban households prefer private education, making it a high-potential sector for expansion.
Policy Reforms & FDI Allowance
The Government of India allows 100% FDI under the automatic route in the education sector. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 also encourages private participation, edtech expansion, and global collaboration.
Internationalization of Indian Education
NEP enables foreign universities to set up campuses in India, bringing global players into Indian metros and Tier-II cities alike.
Why Punjab Is a Rising Star for Education Sector Investment
While metros like Delhi and Bangalore are saturated, states like Punjab present untapped potential—especially in cities like Mohali, Ludhiana, and Amritsar. Punjab’s government has actively promoted education as a key pillar of its growth strategy through policy support, public-private partnerships, and infrastructure expansion.
What Makes Punjab Attractive
Young, Aspiring Population
Punjab has one of the highest youth literacy rates and a strong culture of education-driven mobility evident in the state’s leadership in students going abroad.
Progressive Government Support
Invest Punjab offers fast-track clearances and single-window systems for investors in education. Punjab Education Reforms Initiatives like Sikhya Kranti foster innovation, partnerships, and campus development.
Untapped Rural Demand
Punjab’s rural areas, with rising incomes and digital penetration, are underserved markets where private schools, coaching centres, and EdTech solutions can expand rapidly.
Focus on Skill Development & Employability
With a strong industrial base and rising MSME activity, Punjab is also pushing vocational and skilling programs. The Punjab Skill Development Mission (PSDM) offers a great partner ecosystem for technical institutes.
The Education Cost Landscape
Why Education is Becoming More Expensive in India
Escalating Tuition and Institutional Costs
Private institutions are consistently increasing fees to fund infrastructure upgrades, better teacher salaries, and smart classrooms. These enhancements while improving the quality of education translate into increased costs for parents.
Rising Parental Expectations
Aspirational parents are seeking global-standard education, with advanced teaching methodologies, extracurricular exposure, and international linkages. This demand for quality naturally drives prices higher.
Growth of Private Institutions
India has witnessed a surge in private schools and colleges, which often operate independently without government aid. These institutions typically charge premium fees for digital tools, international tie-ups, and personalized programs.
Coaching and Exam Preparation Costs
Entrance exams such as JEE, NEET, and UPSC are nearly impossible to crack without external coaching. These preparatory classes, mock tests, and special materials form an expensive secondary education economy.
Digital Learning Expenses
Post-COVID, online learning has become mainstream too. Subscriptions to ed-tech platforms, and costs of tablets, laptops, and internet connectivity have added new financial burdens to already-stretched education budgets.
Study Abroad Aspirations
An increasing number of Indian students are looking overseas for higher education. While beneficial, it comes with high tuition, travel, and living expenses, often running into tens of lakhs annually.
Inflation and Operational Overheads
General inflation affects everything—teacher salaries, electricity, real estate, and maintenance. Schools and colleges pass on these rising operational expenses directly to students and parents.
Types of Schools in India
India’s educational landscape is broad and varied, offering several options across different income levels and pedagogical philosophies.
| Type | Features | Appx Cost Range (Annual) |
| Government/Public Schools | Low-cost, funded by central/state governments | ₹500–₹5,000 |
| Private Schools | Modern amenities, better infrastructure | ₹30,000–₹2,00,000 |
| International Schools | Global curriculum (IB/Cambridge), elite exposure | ₹2,00,000–₹10,00,000 |
| Boarding Schools | Residential, holistic development | ₹1,00,000–₹5,00,000+ |
| Special Education Schools | Support for differently-abled children | ₹10,000–₹1,50,000 |
| Distance/Open Schools | Flexibility for working students or remote learners | ₹1,000–₹10,000 |
| Religious/Gurukul Schools | Faith-based, traditional values | ₹1,000–₹20,000 |
| Homeschooling/Alternative | Customized, experiential learning | Varies widely |
Public vs Private Education: The Cost Divide
Why Private Education is More Expensive
- Modern Infrastructure: Smart boards, science labs, auditoriums.
- Well-Paid Teachers: Competitive salaries to attract top faculty.
- Global Exposure: Exchange programs, advanced curriculum.
- Technology: AI tools, learning apps, e-classrooms.
- Self-Financed: Lack of government funding drives costs up.
Why Public Education is More Affordable
- Government Funding: Covers salaries, infrastructure.
- Subsidies: Tuition and meals often free or nominal.
- Scholarship Schemes: Especially for underprivileged students.
- Basic Infrastructure: Less investment in frills, more focus on access.
How Much Does Education Actually Cost in India?
| Education Level | Government Institutions | Private Institutions |
| Primary to Class 12 | ₹500–₹5,000/year | ₹30,000–₹2,00,000/year |
| Undergraduate | ₹10,000–₹50,000/year | ₹1,00,000–₹5,00,000/year |
| Engineering/Medical | ₹50,000–₹2,00,000/year | ₹2,00,000–₹10,00,000/year |
| Postgraduate | ₹20,000–₹2,00,000/year | ₹2,00,000–₹15,00,000/year |
| Study Abroad | — | ₹5,00,000–₹50,00,000+ (incl. living costs) |
The Hidden Costs of Education in India
Beyond tuition, several indirect costs strain the family budget:
- Books & Supplies: Stationery, textbooks, and lab kits.
- Transport: Daily commutes or long-distance travel.
- Extracurriculars: Dance, music, sports, robotics.
- Hostel/PG Rent: Especially in Tier-1 cities.
- Digital Devices: Laptops, tablets, headphones, etc.
- Uniforms & Accessories: Mandatory dress codes, ID cards, shoes.
How Guardians are Managing Education Costs
1. Investing Early
- SIPs: Regular savings in mutual funds offer compounded returns over time.
- PPF: Long-term, tax-free savings with guaranteed returns.
- FDs: Safe, short-term investment for near-future needs.
2. Leveraging Government Schemes
- Scholarships: National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship, Post-Matric Scholarship, etc.
- Free Supplies: Mid-day meals, textbooks, uniforms in government schools.
3. Advantage of Education Loans
- Collateral-Free Loans: Available for UG/PG and international studies.
- Interest Subsidy: Government subsidies for low-income households.
- Flexible Repayment: Grace periods and EMIs post-education.
4. Budgeting Wisely
- Cost Planning: Maintain a 5-year education expense roadmap.
- Avoid Unnecessary Spending: Focus on essentials, not vanity add-ons.
- Compare Institutions: Look for quality over brand value.
5. Using Digital Tools Judiciously
- Free Learning Platforms: YouTube, NPTEL, Diksha App.
- Limit Device Costs: Buy shared or refurbished devices if possible.

Opportunities for Investors in India & Punjab’s Education Sector
Whether you’re a global education provider, domestic school chain, skilling company, or EdTech player, India and Punjab offer a range of opportunities:
1. Premium K-12 School Chains
High demand exists in Tier-II/III cities in Punjab for affordable premium schools that combine infrastructure with modern pedagogy.
2. Higher Education & Foreign University Campuses
Punjab is ideal for foreign universities looking to set up campuses under NEP norms. Mohali and Amritsar are being marketed as education hubs with land availability and policy support.
3. EdTech & Hybrid Learning Models
Localized platforms delivering bilingual and curriculum-aligned content in Punjab can capture vast user bases. Public-private partnerships can amplify reach in rural belts.
4. Vocational Training & Finishing Schools
Given Punjab’s industrial economy and migrant workforce, there is high scope for B2B skill training programs in fields like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
5. Affordable Hostels & Student Housing
With an increase in outstation students in cities like Patiala, Ludhiana, and Jalandhar, student housing is a growing ancillary investment area.
Conclusion
While India’s education sector continues to evolve as one of the largest and fastest-growing in the world, Punjab offers a microcosm of this transformation with its ambitious reforms, focus on equitable access, and willingness to collaborate with private and global partners. Rising costs for families signal strong demand, while government policy support and youth aspirations open the door for investors ready to build the schools, universities, and platforms of tomorrow.
Whether you’re a school chain, university, EdTech innovator, or investor, Punjab is positioning itself not just as a beneficiary of India’s education revolution but as a leader in shaping its future.
Reference links
- Invest India https://www.investindia.gov.in/sector/education
- Press Information Bureau – 100% FDI in Education
https://pib.gov.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=181700 - Make in India – Foreign Direct Investment Policy
https://www.makeinindia.com/policy/foreign-direct-investment - Invest Punjab – Official Portal
The Government of Punjab’s official platform for facilitating investments, including in the education sector.
https://investpunjab.gov.in/ - Invest Punjab Blog – Foreign Universities in India
Discusses the potential for foreign universities to establish campuses in India, with a focus on Punjab.
https://investpunjabblog.com/2025/04/09/indias-next-education-leap-why-foreign-universities-must-invest-but-with-purpose/ - Invest Punjab Blog – Foreign School Chains in India and Punjab
Explores the business case for foreign school chains to invest in India and Punjab.
https://investpunjabblog.com/2024/12/19/foreign-school-chains-in-india-and-punjab-a-business-case/ - Invest India – Education Sector Blog
Highlights the catalysts driving growth in India’s education sector.
https://www.investindia.gov.in/team-india-blogs/examining-catalysts-change-indias-rising-education-sector - Invest India – Education Market Size Projection
Discusses the projected growth of India’s education market, estimating it to reach USD 313 billion by 2030.
https://www.investindia.gov.in/blogs/impact-education-policy-indias-gdp-growth-strengthening-foundation-thriving-nation
